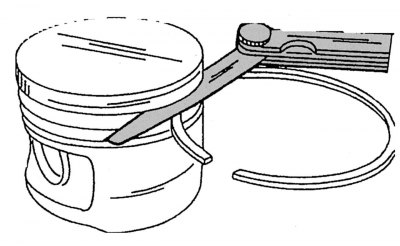
Pic. 58. Measurement of vertical clearances in the grooves of the piston rings using a feeler gauge
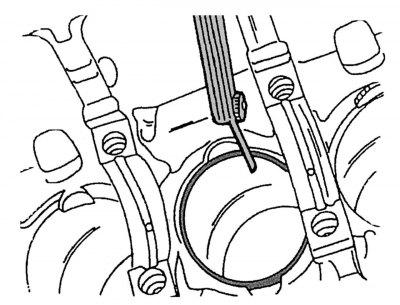
Pic. 59. Measurement of gaps in the locks of piston rings located in the engine cylinders
Carry out a thorough check of all details. If there are scoring, scratches or signs of wear, replace them with new ones. Measure the vertical clearance in the piston ring grooves with a feeler gauge inserted between the piston ring plane and the piston ring groove plane, as shown in fig. 58 (the grooves must be thoroughly cleaned before this, for this you can, for example, use a broken piston ring). If the measurement results show that the gaps in the upper rings exceed 0.20 mm, in the middle - 0.15 mm and in the oil scraper - 0.10 mm, then this indicates wear on the piston rings or pistons. Then, from the inside of the engine crankcase, it is necessary to insert the piston rings one by one into the cylinder bores, and with the inverted piston from above, move them down so that they are located horizontally and are at a distance of 20 mm from the lower edge of the cylinder liners. After that, use a feeler gauge to measure the gaps in the piston ring locks, as shown in Fig. 59. On all rings, this gap is 0.20–0.40 mm. The maximum allowable wear for the locks of the upper rings should not exceed 1.5 mm, for the remaining rings - 1.0 mm.
Check piston pins and connecting rod bushings for wear and tear. In this case, a single replacement of a faulty connecting rod is allowed, however, the mass of the new connecting rod should not differ from the mass of the replaced connecting rod by more than 5 g. We recommend replacing the bushings in the upper heads of the connecting rods at specialized service stations.
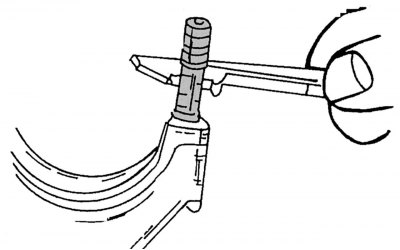
Pic. 60. Measurement of the diameters of the pliable part of the bolts of the connecting rod bearing caps
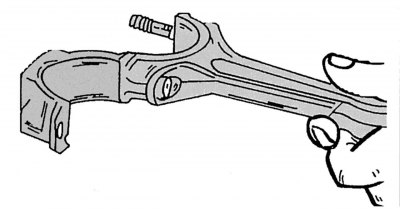
Pic. 61. Control rod for ease of movement
Before reusing the bolts of the connecting rod bearing caps, it is necessary to measure the diameters of their thin parts using a vernier caliper (pic. 60). If the measured bolt diameters are less than 7.1 mm, then such bolts must be replaced, which should be carried out according to the instructions below. Before replacing the bolts, one more check should be made, which is as follows: the connecting rod bearing cap is seated on one bolt and rotated to the side so that the connecting rod and the bearing cap turned to the side are on a horizontal axis, as shown in Fig. 61. If the bearing cap falls down under its own weight, then this connecting rod must be replaced with a new one. Otherwise, the bolts must be replaced. In the connecting rod tester, all connecting rods should be checked for twisting and bending, the values of which should not exceed the minimum allowable. To perform this work, it is also recommended to contact a specialized service station. When checking pistons and connecting rods, there are the following recommendations.
It is not recommended to reuse connecting rods that were once overheated due to bearing failure (connecting rods with tint color).
The connecting rods and connecting rod bearing caps are matched and marked.
New connecting rods are supplied with bored bushings in the upper heads, they can be immediately installed on the engine.
Install the connecting rod bearing caps with liners on the bolts and measure the inner diameter of the bearings using an inside gauge. If the result obtained exceeds 51.619 mm or some taper is detected, then the bearing surface of the connecting rod bearing cap can be corrected on a flat plate up to 0.02 mm.
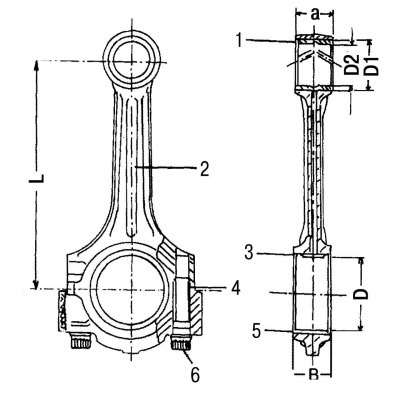
Pic. 62. Connecting rod: 1 - bushing of the upper head of the connecting rod; 2 - connecting rod; 3 - upper bearing shell; 4 - elastic clamping pins; 5 - lower bearing shell; 6 — a bolt of a cover of a rod bearing; L=145mm; B=24.0 mm; D=47.95 mm; D1=29.50 mm; D2=26.0 mm (tolerance 0.018–0.024 mm)
If the connecting rod is in perfect condition, and an increased clearance is found in the piston pin, then it is necessary to replace the bushing in the upper head of the connecting rod by pressing out the old one and pressing in the new one. In this case, special attention must be paid to the location of the oil hole in the bushing. It should be in line with the arrow indicated in fig. 62. After pressing a new bushing into the upper head of the connecting rod, it must be expanded to the diameter D2 indicated in fig. 62. This figure indicates the allowable diameter.
