Car engine repair Mercedes Sprinter I (903)
General description of engines
Diesel engines of 2.3 and 2.9 liters, designated as 601 and 602, were previously installed on other Mercedes-Benz vehicles with the only difference that now the 602...
Diesel engines of 2.3 and 2.9 liters, designated as 601 and 602, were previously installed on other Mercedes-Benz vehicles with the only difference that now the 602...
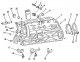
Dismantling the power unit
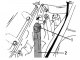
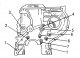
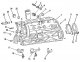
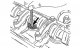
Pic. 14. Dismantling the power unit A lifting hoist or hand winch is required to dismantle the power unit. The power unit is removed forward after removing all shown in...
Pic. 14. Dismantling the power unit A lifting hoist or hand winch is required to dismantle the power unit. The power unit is removed forward after removing all shown in...
Installation of the power unit
The installation of the power unit on the car is carried out in the reverse order of removal, taking into account the following: check for damage and, if necessary,...
The installation of the power unit on the car is carried out in the reverse order of removal, taking into account the following: check for damage and, if necessary,...
Engine disassembly
All diesel engines are very demanding on the cleanliness of maintenance and repair. When performing any work on these engines, make sure that nothing else gets into...
All diesel engines are very demanding on the cleanliness of maintenance and repair. When performing any work on these engines, make sure that nothing else gets into...
Cylinder head — general description
The cylinder head is cast from aluminum alloy. It provides channels for the circulation of coolant, oil, air necessary for the combustion of fuel, exhaust gases. Glow...
The cylinder head is cast from aluminum alloy. It provides channels for the circulation of coolant, oil, air necessary for the combustion of fuel, exhaust gases. Glow...
Removal and installation of a head of the block of cylinders
The cylinder head may only be removed when the engine is cold. The cylinder head is removed together with the exhaust manifold, while the intake manifold must be...
The cylinder head may only be removed when the engine is cold. The cylinder head is removed together with the exhaust manifold, while the intake manifold must be...
Dismantling of a head of the block of cylinders
The operations for replacing the cylinder head are described below. If only repair of the valves is to be carried out, the description of other activities may be...
The operations for replacing the cylinder head are described below. If only repair of the valves is to be carried out, the description of other activities may be...
Cylinder head repair
All parts of the cylinder head should be checked for wear. Thoroughly clean the mating surface of the cylinder head (sometimes sticky fragments of the gasket remain)....
All parts of the cylinder head should be checked for wear. Thoroughly clean the mating surface of the cylinder head (sometimes sticky fragments of the gasket remain)....
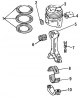
Pistons and connecting rods — removal
Pic. 47. Piston with a chamber made on it (1) combustion The pistons are made of a special aluminum alloy. Each piston has a star-shaped combustion chamber 1 (pic. 47)...
Pic. 47. Piston with a chamber made on it (1) combustion The pistons are made of a special aluminum alloy. Each piston has a star-shaped combustion chamber 1 (pic. 47)...
Cylinder Liner Measurement
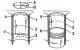
To measure cylinder liners in the middle and bottom, a special cylinder gauge is required (caliper). Without this device, the following work will not be possible. Pic....
To measure cylinder liners in the middle and bottom, a special cylinder gauge is required (caliper). Without this device, the following work will not be possible. Pic....
Checking pistons and connecting rods
Pic. 58. Measurement of vertical clearances in the grooves of the piston rings using a feeler gauge Pic. 59. Measurement of gaps in the locks of piston rings located in...
Pic. 58. Measurement of vertical clearances in the grooves of the piston rings using a feeler gauge Pic. 59. Measurement of gaps in the locks of piston rings located in...
Assembly of pistons and connecting rods
Pic. 54. Piston and connecting rod after disassembly: 1 - piston rings; 2 — lock rings of a piston pin; 3 - piston; 4 - piston pin; 5 - connecting rod; 6 - bearing...
Pic. 54. Piston and connecting rod after disassembly: 1 - piston rings; 2 — lock rings of a piston pin; 3 - piston; 4 - piston pin; 5 - connecting rod; 6 - bearing...
Installation of pistons with connecting rods in cylinders
When installing pistons with connecting rods in the engine cylinders, the following operations must be performed: lubricate the inner surfaces of the cylinders; lay out...
When installing pistons with connecting rods in the engine cylinders, the following operations must be performed: lubricate the inner surfaces of the cylinders; lay out...
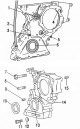
Cover of the mechanism of a drive of a camshaft
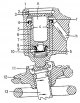
Pic. 43. The cover of the camshaft drive mechanism and its attachments: 1 - alternator mounting bolt, 45 Nm; 2 - alternator; 3 - bolt, 25 Nm; 4 - washer; 5 — a bolt of...
Pic. 43. The cover of the camshaft drive mechanism and its attachments: 1 - alternator mounting bolt, 45 Nm; 2 - alternator; 3 - bolt, 25 Nm; 4 - washer; 5 — a bolt of...
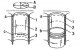
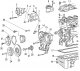
General Description — Cylinder Block
Pic. 65. Parts installed on the cylinder block: 1 - connecting fitting; 2 - threaded nozzle; 3 - connecting fitting for draining the coolant, on the right side; 4, 5 -...
Pic. 65. Parts installed on the cylinder block: 1 - connecting fitting; 2 - threaded nozzle; 3 - connecting fitting for draining the coolant, on the right side; 4, 5 -...
Removal and installation of plugs of the block of cylinders
Pic. 67. The front of the cylinder block: 1 - spring tension pin; 2 — a basic finger of a chain damper; 3 - steel ball with a diameter of 17 mm; 4 - oil spray nozzle; 5...
Pic. 67. The front of the cylinder block: 1 - spring tension pin; 2 — a basic finger of a chain damper; 3 - steel ball with a diameter of 17 mm; 4 - oil spray nozzle; 5...
Piston clearance measurement
To determine the working clearance of the pistons, it is necessary to measure their diameters and record the results. To determine the clearance, measure the cylinder...
To determine the working clearance of the pistons, it is necessary to measure their diameters and record the results. To determine the clearance, measure the cylinder...
Changes in the design of the cylinder block, made as a result of modernization
Pic. 71. Location of the oil spray nozzles of the piston cooling system Listed below are some of the design changes made to the 601 and 602 family engines in case you...
Pic. 71. Location of the oil spray nozzles of the piston cooling system Listed below are some of the design changes made to the 601 and 602 family engines in case you...
Crankshaft and flywheel — general information
The crankshaft is designed to convert the reciprocating motion of the pistons into rotational motion. For added rigidity, each crankpin sits between two main bearings...
The crankshaft is designed to convert the reciprocating motion of the pistons into rotational motion. For added rigidity, each crankpin sits between two main bearings...
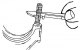
Removing the crankshaft
To remove the crankshaft, you must remove the engine from the car. The removal process must be carried out as follows: disconnect the gearbox from the engine. When...
To remove the crankshaft, you must remove the engine from the car. The removal process must be carried out as follows: disconnect the gearbox from the engine. When...
Checking the crankshaft
The crankshaft must be checked in the following order: carry out a thorough inspection of the crankshaft for wear and deformation, measure the journals of the main and...
The crankshaft must be checked in the following order: carry out a thorough inspection of the crankshaft for wear and deformation, measure the journals of the main and...
Installing the crankshaft
The installation of the crankshaft must be carried out in the following order: Wipe the seats of the main bearings of the crankshaft and insert liners with holes and...
The installation of the crankshaft must be carried out in the following order: Wipe the seats of the main bearings of the crankshaft and insert liners with holes and...
Flywheel or drive plate (models with automatic transmission)
The engine is equipped with a combined flywheel with a torsional vibration damper (damper). The meaning of such a flywheel design is to smooth and prevent the...
The engine is equipped with a combined flywheel with a torsional vibration damper (damper). The meaning of such a flywheel design is to smooth and prevent the...
Belt pulley and crankshaft vibration damper
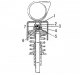
Pic. 76. Crankshaft and mating parts on the example of the 602 engine (similar parts are used on the 601st engine): 1 — a bolt of fastening of an asterisk of a chain...
Pic. 76. Crankshaft and mating parts on the example of the 602 engine (similar parts are used on the 601st engine): 1 — a bolt of fastening of an asterisk of a chain...
Rear oil seal of the crankshaft and its holder
Pic. 65. Parts installed on the cylinder block: 1 - connecting fitting; 2 - threaded nozzle; 3 - connecting fitting for draining the coolant, on the right side; 4, 5 -...
Pic. 65. Parts installed on the cylinder block: 1 - connecting fitting; 2 - threaded nozzle; 3 - connecting fitting for draining the coolant, on the right side; 4, 5 -...
Forward cuff of a cranked shaft
Pic. 44. Cover of the camshaft drive mechanism with the indication of individual parts (the details of the lid are shown below): 1 - support pin of the generator drive...
Pic. 44. Cover of the camshaft drive mechanism with the indication of individual parts (the details of the lid are shown below): 1 - support pin of the generator drive...
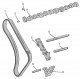
Camshaft Drive Mechanism — General Description
Pic. 95 a. Camshaft drive chain tensioner: 1 - cork; 2 - plug gasket; 3 - ball; 4 - spring seat; 5 - pressure spring; 6 - finger; 7 - unloading valve; 8 - sealing ring;...
Pic. 95 a. Camshaft drive chain tensioner: 1 - cork; 2 - plug gasket; 3 - ball; 4 - spring seat; 5 - pressure spring; 6 - finger; 7 - unloading valve; 8 - sealing ring;...
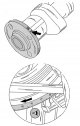
Removal and installation of the camshaft drive chain tensioner
The chain tensioner is located on the side, on the right side of the cylinder head. The force in the chain tensioner is generated by the spring force and engine oil...
The chain tensioner is located on the side, on the right side of the cylinder head. The force in the chain tensioner is generated by the spring force and engine oil...
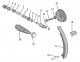
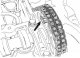
Removal and installation of the camshaft drive chain
The camshaft and fuel pump are driven by a two-row drive chain. The camshaft and fuel pump drive sprockets have twice as many teeth as the crankshaft drive sprocket. Two...
The camshaft and fuel pump are driven by a two-row drive chain. The camshaft and fuel pump drive sprockets have twice as many teeth as the crankshaft drive sprocket. Two...
Removal and installation of the chain tensioning shoe
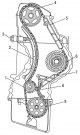
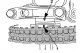
Pic. 96. Camshaft drive mechanism assembly: 1 - crankshaft sprocket; 2 - chain tension shoe; 3 - chain tensioner; 4 - camshaft drive sprocket; 5 - chain damper; 6 - fuel...
Pic. 96. Camshaft drive mechanism assembly: 1 - crankshaft sprocket; 2 - chain tension shoe; 3 - chain tensioner; 4 - camshaft drive sprocket; 5 - chain damper; 6 - fuel...
Dismantling and installation of drive chain dampers
Pic. 95 b. Other parts of the camshaft drive mechanism: 1 - double-row drive chain; 2 - landing pin; 3 - thrust washer of the camshaft; 4 - camshaft; 5 - chain dampers;...
Pic. 95 b. Other parts of the camshaft drive mechanism: 1 - double-row drive chain; 2 - landing pin; 3 - thrust washer of the camshaft; 4 - camshaft; 5 - chain dampers;...
Removal and installation of an asterisk of a cranked shaft
Removal and installation of the crankshaft sprocket must be carried out in the following order: remove all components and parts that prevent access to the end of the...
Removal and installation of the crankshaft sprocket must be carried out in the following order: remove all components and parts that prevent access to the end of the...
Removal and installation of a camshaft
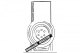
Pic. 108. Numeric identifier indicating the corresponding modification or size group of the camshaft (up). Correct direction of rotation of the crankshaft (at the...
Pic. 108. Numeric identifier indicating the corresponding modification or size group of the camshaft (up). Correct direction of rotation of the crankshaft (at the...
Gas distribution mechanism
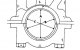
Pic. 102. The location of the marks when the piston of the first cylinder is at TDC The gas distribution mechanism cannot be adjusted. That is why it is necessary to...
Pic. 102. The location of the marks when the piston of the first cylinder is at TDC The gas distribution mechanism cannot be adjusted. That is why it is necessary to...
Hydraulic valve lifters — device
Pic. 114. Valve pusher: 1 - rocker; 2 - retaining ring; 3 - washer; 4 - cap; 5 - push rod; 6 - guide sleeve; 7 - guide channel of the ball; 8 - a ball with a diameter of...
Pic. 114. Valve pusher: 1 - rocker; 2 - retaining ring; 3 - washer; 4 - cap; 5 - push rod; 6 - guide sleeve; 7 - guide channel of the ball; 8 - a ball with a diameter of...
Checking the health of hydraulic pushers
The noise of the hydraulic pushers is almost inaudible for the reason that they are in constant contact with the camshaft. With the appearance of noise from the camshaft...
The noise of the hydraulic pushers is almost inaudible for the reason that they are in constant contact with the camshaft. With the appearance of noise from the camshaft...
Removal and installation of hydropushers
Pic. 116. Valve with hydraulic pusher (cross section): 1 - pressure finger (stock); 2 - retaining ring; 3, 5 - pressure springs; 4 - ball; 6 - guide sleeve; 7 - ball...
Pic. 116. Valve with hydraulic pusher (cross section): 1 - pressure finger (stock); 2 - retaining ring; 3, 5 - pressure springs; 4 - ball; 6 - guide sleeve; 7 - ball...
Diesel engine specifications
208D (901.3) — 601.943 208D (902.3) — 601.943 308D (903.3) — 601.943 408D (904.3) — 601.943 212D (901.4) — 602 DE 29 LA (602.980) 312D (903.4) — 602 DE 29 LA (602.980)...
208D (901.3) — 601.943 208D (902.3) — 601.943 308D (903.3) — 601.943 408D (904.3) — 601.943 212D (901.4) — 602 DE 29 LA (602.980) 312D (903.4) — 602 DE 29 LA (602.980)...
This section is available on: russian, bulgarian, belarusian, ukrainian, serbian, croatian, romanian, polish, slovak, hungarian
More similar sections for repairing other models
☛ Power unit: Engine overhaul car Mercedes 190 (W201) (1982-1993)
☛ Power unit: Engine overhaul car Mercedes W124 (1984-1995)
☛ Power unit: Engine repair car Mercedes W220 (1998-2005)
Link in different formats to this section
TEXTHTMLBB Code
- General information
- User manual
- Maintenance
- Diesel engine OM646
- Engine repair
- Cooling and lubrication system
- Power and exhaust system
- Transmission
- Clutch
- Car gearbox
- Chassis
- Front suspension
- Rear suspension
- Steering
- Brake system
- Body
- Body elements
- Electrical equipment
- Equipment and devices
- Security systems
- Electrical circuits
- General information
- User manual
- Maintenance
- Petrol engines 2.0 l
- Engine repair
- Lubrication system
- Cooling system
- Power and control system
- Petrol engines 2.8 l
- Engine repair
- Lubrication system
- Cooling system
- Power and control system
- Diesel engines 2.3 l
- Engine repair
- Cooling system
- Lubrication system
- Turbocharging and recycling
- Power and control system
- Diesel engines 2.2 l
- Engine repair
- Cooling system
- Lubrication system
- Turbocharging and recycling
- Power and control system
- Transmission
- Clutch
- Mechanical gearbox
- Automatic gearbox
- Chassis
- Front suspension and wheels
- Rear suspension
- Steering
- Brake system
- Body
- Exterior (external elements)
- Interior (internal elements)
- Electrical equipment
- Equipment and devices
- Heater and air conditioner
- Electrical circuits
- General information
- Introduction to the guide
- Maintenance
- Power unit
- Engine repair
- Lubrication system
- Cooling system
- Power and exhaust system
- Transmission
- Clutch
- Mechanical gearbox
- Automatic gearbox
- Front axle
- Rear axle and cardan
- Chassis
- Car suspension
- Steering
- Brake system
- Tires and wheels
- Electrical equipment
- Equipment and devices
- Headlights and lighting
- Power devices
- Electrical circuits
MercedesMan.ru © 2017–2024 · Mobile version · Read about Mercedes · Sitemap: EN BG BY UA RS HR RO PL SK HU · Feedback · Site search · Bookmark
A-Class (W168) · C-Class (W201) · C-Class (W202) · C-Class (W203) · E-Class (W123) · E-Class (W124) · E-Class (W210) · G-Class (W463) · M-Class (W163) · S-Class (W116, petrol) · S-Class (W126, petrol) · S-Class (W140) · S-Class (W220) · Sprinter · Vito 1 · Vito 2 ·