Voltage measurement
The presence of voltage in the circuit can be detected using a test lamp or voltage indicator. Such a device, however, can only detect the presence, but not measure the voltage. To measure voltage, it is necessary to use a voltmeter, which is always an integral part of a multifunctional measuring device.
First of all, you need to set the scale of the device depending on the expected values of the measured voltage. Typically, the voltage does not exceed 14 V. An exception is the ignition system, in which the voltage can reach up to 30,000 V. This voltage can only be measured with a special measuring device or using an oscilloscope.
While a voltmeter only needs to be turned on when used in specially designed measuring devices, there are a number of steps that need to be taken when using a multifunction meter. First of all, the range switch must be set to DC (D.C) unlike AC mode (alternating current). Then you need to choose the desired scale. Since there are no voltages higher than 14 V on the car, except for the ignition voltage, the upper limit of voltage measurements should be slightly higher (about 15-20 V). If it is known in advance that the measured voltage will be significantly lower, for example in the 2 V range, the voltage measurement range can be switched to a lower one in order to obtain a higher measurement accuracy. If the measured voltage is higher than the selected measurement range, the device may fail.
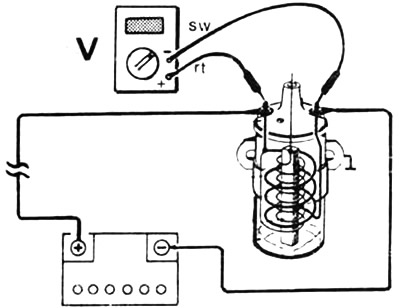
Connect the meter leads parallel to the element. The red wire is connected to the positive terminal, while the black wire is connected to the ground terminal or chassis (mass) engine, for example, to the engine block.
Check: If the engine does not start due to poor rotation of the starter, it is necessary to measure the voltage of the battery while the starter is running. To do this, connect the red wire (+) voltmeter to the positive battery terminal, and the black wire (-) - to the earthed battery wire. Then ask an assistant to turn on the starter and take the voltage readings on the instrument scale. If the voltage is below 7V, the battery should be checked and possibly recharged before the starter is turned on again.
Current measurement
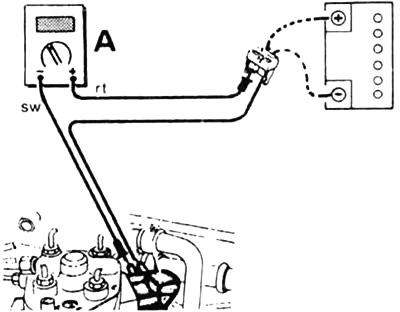
To measure the amount of current in an electrical circuit, it must be broken and a measuring device inserted into the circuit break (ammeter). In this case, the connector is removed and the red wire (+) ammeter is connected to a current-carrying wire (terminal 30, terminal 15). black wire (-) connects to the pin to which the broken wire was previously connected. The ground contacts between the electrical consumer and the connector must be connected to an additional wire.
Example: "Battery self-discharge".
Note: Never measure the current in the wire leading to the starter (about 150 A) or to starter sockets in a diesel engine (about 60 A), using a conventional ammeter. Large currents can damage the measuring instrument. In the repair shop, an ammeter with current pliers is used, which covers a current-carrying wire and measures the strength of this current by induction.
Resistance measurement
Before starting the procedure for measuring the resistance of an electrical circuit, you should make sure that there is no voltage at the resistance measurement points. Therefore, the first step is always to disconnect all electrical connectors, turn off the ignition, disconnect the wire or block associated with the battery, or disconnect the battery itself. Otherwise, the measuring device may be damaged.
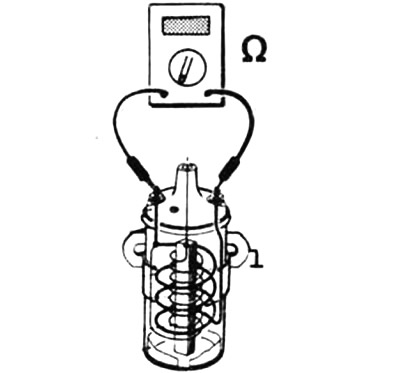
An ohmmeter is connected to two connections of an electrical element or to two ends of an electrical wire. It doesn't matter which wire (+/-) ohmmeter will be connected to one or another contact of the device.
On-vehicle resistance measurement is mainly carried out in two areas:
1. Checking the resistance of the circuit with a constant or variable level of values (resistance). Example: checking the resistance of a temperature sensor when disconnecting the connector from this sensor and connecting an ohmmeter to the gap between the connector and the sensor. Turn on the ohmmeter on the scale within which the estimated resistance values \u200b\u200bwill be measured, and compare the value obtained with the values \u200b\u200bgiven in the reference table.
2. "continuous" checking the electrical wire, switch, or filament of the electrical heater. This test allows you to determine if there is a break in the car wire and if the connected electrical devices can work. If the circuit resistance is 0 ohm, "continuity" circuit is observed and, therefore, the measured device or wire is in good order. If there is an open in the circuit, the measuring device will show an infinitely large resistance.
