The turbocharger consists of a centrifugal air pump and a turbine connected by a common rigid axis to each other. Both of these elements rotate in the same direction and at the same speed. The energy in the exhaust gas flow, which is not used in conventional engines, is converted here into torque, which drives the turbocharger. Exhaust gases leaving the engine cylinders are at high temperature and pressure. They accelerate to high speed and come into contact with the turbine blades, which converts their kinetic energy into mechanical energy of rotation. This energy conversion is accompanied by a decrease in the temperature of the exhaust gases and their pressure. The turbocharger sucks air through the air filter, compresses it and delivers it to the engine cylinders. The amount of fuel that can be mixed with air can be increased, allowing the engine to develop more power.
The turbocharger is installed under the exhaust manifold. To lubricate the turbocharger, engine oil is supplied under pressure through a special pipeline from the cylinder head. The turbocharger has a relief valve and a vacuum diaphragm, which serves to limit the pressure supplied by the turbocharger to the intake manifold.
Since the turbocharger operates at high speeds, care and cleanliness must be observed to prevent contaminants from entering the turbocharger and damaging it.
Attention! Before disconnecting any elements from the turbocharger, clean them thoroughly. To protect against contamination, place the elements removed from the turbocharger in a sealed container. To prevent dirt from entering the turbocharger, close the air passages of the turbocharger.
Removing
Turbocharger
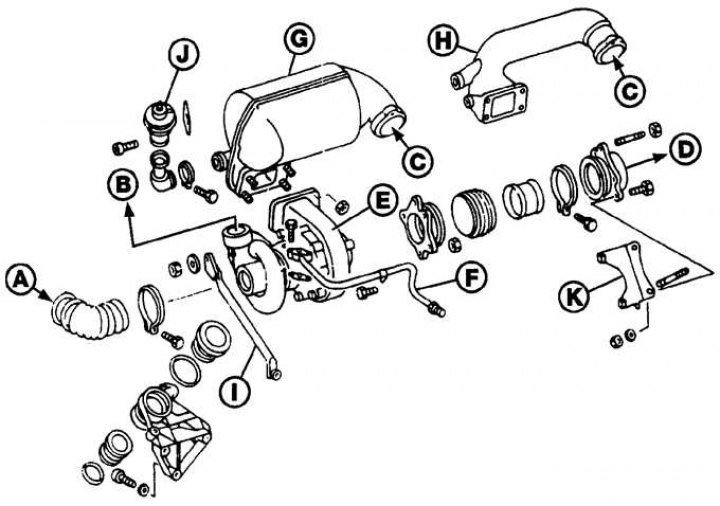
A - from the air filter; B - to the intake manifold; C - from the exhaust manifold; D - to the exhaust pipe; E - turbocharger; F - oil supply pipe; G is an oxidizing agent; H - exhaust gas supply pipe; I - emphasis; J - EGR valve; K - bracket
1. Remove the ground wire from the battery.
2. Release the clips and remove the mudguard from the bottom of the engine compartment.
3. Remove the air filter. On models with an oxidizer, unscrew the screws and remove the heat shield installed between the air filter and the oxidizer.
4. Loosen the clamps and remove the air duct connecting the turbogenerator to the air filter (see picture).
5. Label and disconnect the vacuum hoses from the diaphragm housing and the EGR valve.
6. If equipped, loosen the clamps and remove the corrugated hose from the EGR valve base.
7. Unscrew the nuts and remove the oxidizer together with the bracket from the exhaust manifold.
Attention! On vehicles without an oxidizer, an exhaust gas supply pipe to the turbocharger is installed.
8. Loosen the clamps and remove the air lines connecting the turbocharger to the intake manifold.
9. Loosen the clamps and remove the mixing tube located at the base of the EGR valve from the turbocharger.
10. Unscrew the union nuts and disconnect the oil supply and return pipes from the turbocharger. Remove seals. Remove the oil feed pipe from the mounting bracket on the intake manifold.
11. Unscrew the nuts and separate the exhaust pipe from the turbocharger. Remove the gasket.
12. Unscrew the bolts and remove the turbocharger from the bracket.
Installation
1. Installation is carried out in the reverse order of removal, taking into account the following points.
2. Before tightening the turbocharger-to-bracket bolts, install the exhaust manifold-to-turbocharger nuts.
3. Apply a thin layer of high temperature grease to the threads and heads of the new oxidizer connecting pipe bolts, then screw in the bolts and tighten them to the specified torque.
4. Using clean engine oil, flush the turbocharger oil supply pipe and turbocharger oil inlet. Install the oil pickup pipe and tighten the connecting nuts to the required torque.
5. Connect the vacuum hoses as marked previously.
6. Start the engine at idle and let it run at this speed for at least 1 minute to allow oil to flow to the turbocharger bearings.
