Removing piston rings
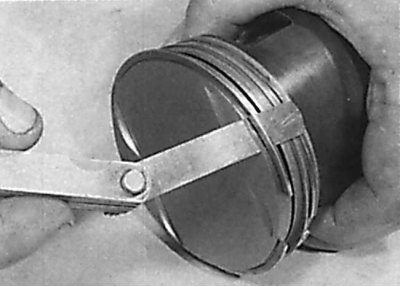
Removing the piston pin circlip

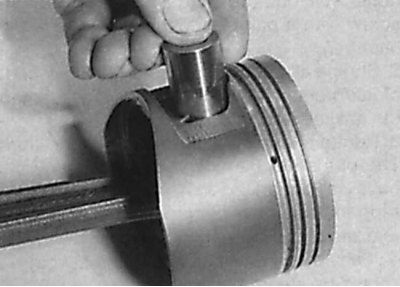
Piston pin removal
Oil hole in connecting rod head
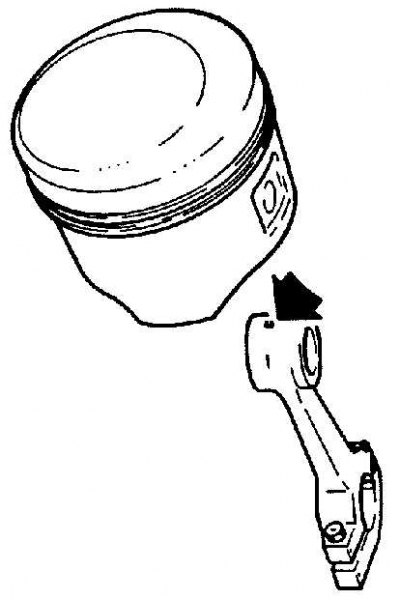
On 4-cylinder gasoline engines and 6-cylinder SOHC engines, the small oil hole in the connecting rod head must be on the drive chain side.
Grooves for liners and protrusion under the piston crown
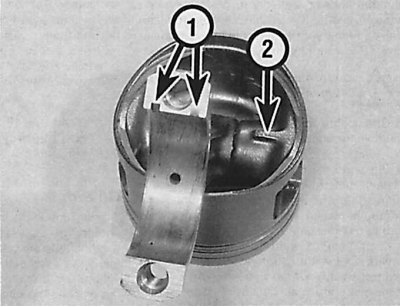
On 6-cylinder DOHC gasoline engines, the bushing grooves (1) must be located on the side of the intake manifold, and the protrusion (2) under the piston crown should be on the flywheel side.
1. Before checking pistons with connecting rods, remove the piston rings from the pistons and thoroughly clean the pistons.
2. To remove the piston rings from the pistons, open the ring and insert two or three old feeler blades evenly around the circumference under the ring and slide the ring off the piston along them. Be careful not to scratch the piston with the ends of the ring. The rings are very brittle and can crack if unclenched too much. The piston ring lips are very sharp, so handle them very carefully to avoid cuts. Keep each set of rings with the pistons to reinstall them.
3. Clean all carbon deposits from the top of the piston.
4. Remove carbon deposits from the piston ring grooves in the piston using the old piston ring.
5. After removing deposits, clean the piston with connecting rod with a suitable solvent and wipe dry.
6. Carefully inspect each piston for cracks around the skirt and piston pin holes.
7. Check for wear on the piston skirt, hole in the piston head, and burns on the top of the piston.
8. Pitting marks on the piston indicate that coolant has entered the combustion chamber. It is necessary to find the cause of the liquid entering the combustion chamber and eliminate it.
9. Measure the piston diameter.
10. Determine the piston clearance in the cylinder, for which subtract the piston diameter from the cylinder diameter and divide by two.
11. Check each connecting rod for wear, cracks, and distortion.
12. The piston pins are fitted with a sliding fit and secured to the piston with two circlips. On these engines, the pistons and connecting rods can be separated as follows.
13. Using the blade of a thin screwdriver, remove the retaining ring from the piston and press out the piston pin by hand. When reinstalling the piston pin, use only new circlips.
14. Check the piston pin and connecting rod bearing for wear.
15. Connecting rods usually do not require replacement unless the engine has seized beforehand.
16. Assemble pistons with connecting rods as follows (see fig. Oil hole in the connecting rod head, Grooves for liners and ledge under the piston crown).
17. On 4-cylinder gasoline engines and 6-cylinder SOHC gasoline engines, the small oil hole at the top of the connecting rod and the arrows on the piston crown must point towards the drive chain.
18. On 6-cylinder DOHC gasoline engines, the connecting rod bearing shell grooves in the connecting rod and cap must be on the intake manifold side and the arrow on the piston crown must point towards the drive chain. The protrusion under the piston crown must point towards the flywheel.
19. On diesel engines, the grooves for the bearing shells in the connecting rod and the connecting rod cap must be on the injection pump side, and the arrow on the piston crown must point towards the drive chain.
20. Lubricate the piston pin and insert it into the piston and connecting rod top end. Check that the piston turns easily and freely on the piston pin, then fix the piston pin with new circlips.
