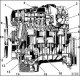
Gasoline car engine Mercedes C-Class (W202)
Specifications of gasoline engines
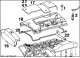
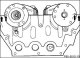
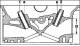
2.2L engine 1. Double roller chain; 2. Oil filling cap; 3. Cylinder head cover; 4. Cylinder head; 5. Piston; 6. Flywheel; 7. Cylinder; 8. Flywheel 9. Oil filter; 10....
2.2L engine 1. Double roller chain; 2. Oil filling cap; 3. Cylinder head cover; 4. Cylinder head; 5. Piston; 6. Flywheel; 7. Cylinder; 8. Flywheel 9. Oil filter; 10....
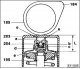
Engine identification number
Based on this number, the vehicle can be identified. It includes model and body variant data. The identification number is embossed in front of the front right seat on...
Based on this number, the vehicle can be identified. It includes model and body variant data. The identification number is embossed in front of the front right seat on...
Removing the engine
The engine is dismantled up together with the gearbox using a crane. Never lower the engine down using a mounting jack, which can cause severe damage to the engine....
The engine is dismantled up together with the gearbox using a crane. Never lower the engine down using a mounting jack, which can cause severe damage to the engine....
Engine installation
1. Check engine mounts, coolant and oil hoses, as well as fuel lines for porosity, cracks, replace if necessary. 2. Check the crankshaft radial bearings and clutch...
1. Check engine mounts, coolant and oil hoses, as well as fuel lines for porosity, cracks, replace if necessary. 2. Check the crankshaft radial bearings and clutch...
Engine ventilation
Engine ventilation is necessary to prevent harmful overpressure from building up in the crankshaft housing. Since the piston rings cannot seal tightly enough, hot gases...
Engine ventilation is necessary to prevent harmful overpressure from building up in the crankshaft housing. Since the piston rings cannot seal tightly enough, hot gases...
Removing the engine (vehicles with air conditioning)
Attention! The air conditioning coolant circuit must not be opened. The coolant contains substances that cause frostbite on contact with the skin. The engine can also be...
Attention! The air conditioning coolant circuit must not be opened. The coolant contains substances that cause frostbite on contact with the skin. The engine can also be...
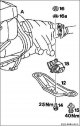
The lower cover of the engine compartment — removal and installation
Removing 1. Raise the car. 2. Unscrew the 6 screws securing the cover (arrows) and remove the bottom cover. Installation 1. Attach the cover and tighten with screws. At...
Removing 1. Raise the car. 2. Unscrew the 6 screws securing the cover (arrows) and remove the bottom cover. Installation 1. Attach the cover and tighten with screws. At...
Cast hole caps (6-cylinder engine)
Cast holes are located on the side of the engine block. They are connected to the coolant channels and closed with tin covers. If the liquid freezes at low temperatures,...
Cast holes are located on the side of the engine block. They are connected to the coolant channels and closed with tin covers. If the liquid freezes at low temperatures,...
Chain tensioner — removal and installation
Attention! If the tensioner loosens on the hexagon, then it must be removed without fail, otherwise the control chain will be over-tightened when screwing. Removing 4...
Attention! If the tensioner loosens on the hexagon, then it must be removed without fail, otherwise the control chain will be over-tightened when screwing. Removing 4...
Cylinder head cover (4-cylinder engine)
Removing 1. Remove the air cleaner cross tube by loosening the sleeve clamps. 2. Remove the engine ventilation hose (22) from the cylinder head housing after loosening...
Removing 1. Remove the air cleaner cross tube by loosening the sleeve clamps. 2. Remove the engine ventilation hose (22) from the cylinder head housing after loosening...
Cylinder head cover (6-cylinder engine)
Removing 1. Remove the air filter. 2. Disconnect the engine ventilation hose (12) from the cylinder head housing after loosening the hose clamp (11). 3. Detach the cover...
Removing 1. Remove the air filter. 2. Disconnect the engine ventilation hose (12) from the cylinder head housing after loosening the hose clamp (11). 3. Detach the cover...
Cylinder head (4-cylinder engine)
Cylinder head bolts Remove the cylinder head only when the engine is cold. The exhaust and intake manifolds remain connected. A defective cylinder head gasket is...
Cylinder head bolts Remove the cylinder head only when the engine is cold. The exhaust and intake manifolds remain connected. A defective cylinder head gasket is...
Cylinder head (2.2 liter engine)
1. Install the camshaft adjuster. To do this, screw the flanged shaft (16) new bolts (wrench size T40). Tighten the bolts as follows: first with a torque wrench with a...
1. Install the camshaft adjuster. To do this, screw the flanged shaft (16) new bolts (wrench size T40). Tighten the bolts as follows: first with a torque wrench with a...
Cylinder head (6-cylinder engine)
The cylinder head can only be disassembled when the engine is cold. The intake and exhaust manifolds remain connected. A defective gasket can be recognized by a number...
The cylinder head can only be disassembled when the engine is cold. The intake and exhaust manifolds remain connected. A defective gasket can be recognized by a number...
Camshafts (4-cylinder engine)
Attention! If the valve control parts are to be used again, they must be installed in the same places. To avoid confusion, it is recommended to make an appropriate panel...
Attention! If the valve control parts are to be used again, they must be installed in the same places. To avoid confusion, it is recommended to make an appropriate panel...
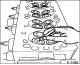
Camshafts — Basic Position Adjustment (4 Cylinders)
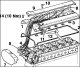
Camshafts 1. Wrench (for turning camshafts); 73. Control circuit; 75. Intake camshaft gear 76. Exhaust camshaft gear; 77. Exhaust camshaft; 78. Intake camshaft; 79....
Camshafts 1. Wrench (for turning camshafts); 73. Control circuit; 75. Intake camshaft gear 76. Exhaust camshaft gear; 77. Exhaust camshaft; 78. Intake camshaft; 79....
Camshafts (6-cylinder engine)
Attention! If the valve control parts are to be used again, they must be installed in the same places. In order not to confuse the parts, we recommend making a panel for...
Attention! If the valve control parts are to be used again, they must be installed in the same places. In order not to confuse the parts, we recommend making a panel for...
Hydraulic Poppet Pushers
All engines are equipped with hydraulic poppets. This reduces the noise in the valve drive and, in addition, does not require adjustment of the valve clearance as part...
All engines are equipped with hydraulic poppets. This reduces the noise in the valve drive and, in addition, does not require adjustment of the valve clearance as part...
Oil seals — removal and installation
Worn valve stem seals can cause increased oil consumption. The caps can also be removed with the cylinder head installed. True, this requires compressed air and a lever...
Worn valve stem seals can cause increased oil consumption. The caps can also be removed with the cylinder head installed. True, this requires compressed air and a lever...
Valves — removal and installation
Removing Attention! If the valve control parts are to be used again, they must be reinstalled. In order not to confuse the parts, make a panel for storing them. 1....
Removing Attention! If the valve control parts are to be used again, they must be reinstalled. In order not to confuse the parts, make a panel for storing them. 1....
Directional valves
In the course of repair work on a cylinder head with leaking valves, treatment or replacement of the valve and valve seat is not enough. Check valve guides for wear. It...
In the course of repair work on a cylinder head with leaking valves, treatment or replacement of the valve and valve seat is not enough. Check valve guides for wear. It...
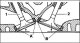
Valve seats in the cylinder head
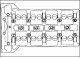
A. Exhaust valve seat ring (1) B. Inlet valve seat ring (2) Valve seats with signs of wear or scorching can be reworked if the corrective angle and seat width are...
A. Exhaust valve seat ring (1) B. Inlet valve seat ring (2) Valve seats with signs of wear or scorching can be reworked if the corrective angle and seat width are...
Cylinder compression check
Compression check allows you to draw conclusions about the condition of the engine. When checking it, you can determine whether the valves or pistons are normal (piston...
Compression check allows you to draw conclusions about the condition of the engine. When checking it, you can determine whether the valves or pistons are normal (piston...
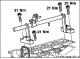
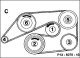
V-belt (4-cylinder engine)
1. Tension roller; 2. Belt pulley crankshaft; 3. Cooling compressor belt pulley (with air conditioning only); 4. Belt pulley of the three-phase current generator; 5....
1. Tension roller; 2. Belt pulley crankshaft; 3. Cooling compressor belt pulley (with air conditioning only); 4. Belt pulley of the three-phase current generator; 5....
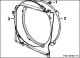
V-belt (6-cylinder engine)
Removing 1. Pull out the locking tab (1) from the fan shroud ring (2). Rotate the casing in the direction of the embossed arrow "open" and remove by turning the fan...
Removing 1. Pull out the locking tab (1) from the fan shroud ring (2). Rotate the casing in the direction of the embossed arrow "open" and remove by turning the fan...
Diagnostics of malfunctions of gasoline engines
If the engine does not start, you need to determine the cause of the malfunction. For it to start at all, two basic prerequisites must be met: the air-fuel mixture must...
If the engine does not start, you need to determine the cause of the malfunction. For it to start at all, two basic prerequisites must be met: the air-fuel mixture must...
General notes on engine overhaul
This section covers engine overhaul operations, including cylinder head and cylinder block parts. The section includes both recommendations regarding the organization...
This section covers engine overhaul operations, including cylinder head and cylinder block parts. The section includes both recommendations regarding the organization...
Repair work without dismantling the engine
Many basic repairs can be performed without removing the engine from the vehicle. Before starting any work, it is highly advisable to flush the engine compartment and...
Many basic repairs can be performed without removing the engine from the vehicle. Before starting any work, it is highly advisable to flush the engine compartment and...
Engine overhaul
It is not always easy to come to the conclusion about the feasibility of overhauling the engine, since it is necessary to be based on a number of indicators. High...
It is not always easy to come to the conclusion about the feasibility of overhauling the engine, since it is necessary to be based on a number of indicators. High...
Engine Overhaul Alternatives
There are a number of options available for a major overhaul. The decision to replace the cylinder block, connecting rod and piston group and crankshaft depends on a...
There are a number of options available for a major overhaul. The decision to replace the cylinder block, connecting rod and piston group and crankshaft depends on a...
Dismantling the engine
If it was decided to dismantle the engine for a major overhaul, or repair of the main components, then certain preparatory measures must be taken. It is extremely...
If it was decided to dismantle the engine for a major overhaul, or repair of the main components, then certain preparatory measures must be taken. It is extremely...
Engine disassembly sequence
It is easiest to disassemble the engine and perform all types of work on a portable stand. Before mounting the engine on the stand, it is necessary to remove the...
It is easiest to disassemble the engine and perform all types of work on a portable stand. Before mounting the engine on the stand, it is necessary to remove the...
This section is available on: russian, bulgarian, belarusian, ukrainian, serbian, croatian, romanian, polish, slovak, hungarian
More similar sections for repairing other models
☛ Power unit: Gasoline engines car Mercedes W163 (1997-2005)
☛ Power unit: Petrol engine V6 car Mercedes W140 (1991-1998)
Link in different formats to this section
TEXTHTMLBB Code
- General information
- Introduction to guide
- User manual
- Maintenance
- Power unit
- Gasoline engines
- Diesel engines
- Cooling system
- Ventilation and heating
- Supply system
- Injection system (gasoline)
- Injection system (diesel)
- Exhaust system
- Ignition and control system
- Charge and launch systems
- Transmission
- Mechanical gearbox
- Automatic gearbox
- Clutch and drive shafts
- Differential
- Chassis
- Brake system
- Car suspension
- Steering
- Body
- Exterior (external elements)
- Interior (internal elements)
- Electrical equipment
- Equipment and devices
- Lighting system
- Electrical diagrams (2000)
- Electrical diagrams (since 2001)
- General information
- User manual
- Driving a car
- Car care
- Maintenance
- Power unit
- Gasoline engines
- Diesel engines
- Lubrication system
- Cooling system
- Heating and ventilation
- Ignition system
- Fuel system
- Injection system (gasoline)
- Injection system (diesel)
- Exhaust system
- Transmission
- Clutch
- Car gearbox
- Chassis
- Suspension, wheels and tires
- Steering
- Brake system
- Body
- Exterior (external elements)
- Interior (internal elements)
- Doors and windows
- Electrical equipment
- Equipment and devices
- Power devices
- Lighting system
- Electrical circuits
- General information
- Introduction to the guide
- Operation and care
- Maintenance (gasoline)
- Maintenance (diesel)
- Troubleshooting
- Power unit
- Petrol engine I4
- Petrol engine V6
- Diesel engines
- Engine overhaul
- Cooling and heating
- Power system (carburetor)
- Injection system (gasoline)
- Injection system (diesel)
- Exhaust system
- Charge and start system
- Ignition system (I4)
- Ignition system (V6)
- Diesel heating system
- Transmission
- Clutch
- Mechanical gearbox
- Automatic gearbox
- Cardan shaft and axle shafts
- Chassis
- Brake system
- Car suspension
- Steering
- Body
- Exterior (external elements)
- Interior (internal elements)
- Doors, locks and windows
- Electrical equipment
- Equipment and devices
- Electrical circuits
MercedesMan.ru © 2017–2024 · Mobile version · Read about Mercedes · Sitemap: EN BG BY UA RS HR RO PL SK HU · Feedback · Site search · Bookmark
A-Class (W168) · C-Class (W201) · C-Class (W202) · C-Class (W203) · E-Class (W123) · E-Class (W124) · E-Class (W210) · G-Class (W463) · M-Class (W163) · S-Class (W116, petrol) · S-Class (W126, petrol) · S-Class (W140) · S-Class (W220) · Sprinter · Vito 1 · Vito 2 ·