Since the piston rings cannot seal tightly enough, combustible gases enter the crankcase. A mixture of hot oil and fuel vapors can create excessive pressure that adversely affects the crank mechanism. To avoid this, the gases must be sucked off via the connecting hose of the motor and incinerated.
Closed motor ventilation does not require maintenance.
Functioning
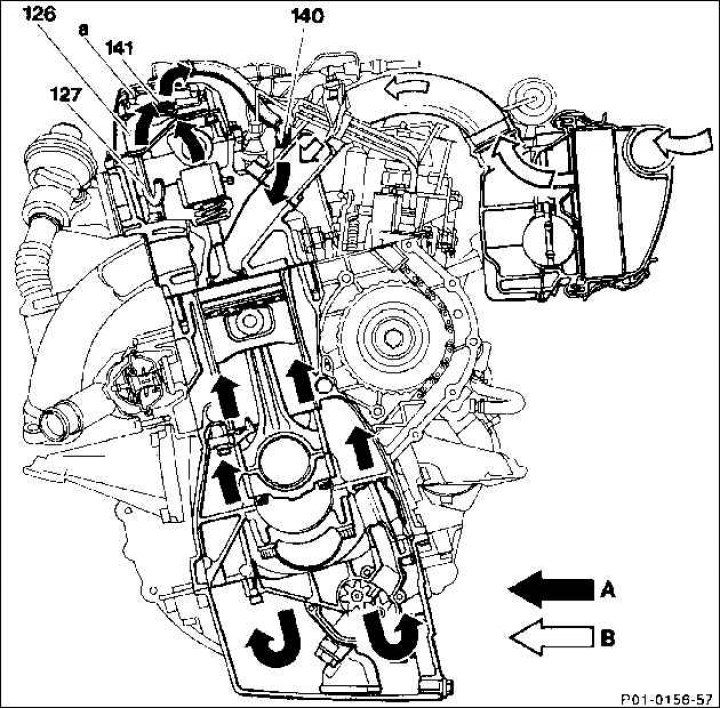
126. Oil separator; 127. Recirculation pipe; 140. Distribution pipe; 141. Pressure control valve; A. Ventilation hole with a diameter of 3 mm; A. Purge gases; B. Fresh air
Hot gases rush through the oil separator (126) into the cylinder head cover and through the pipeline (140) into the suction pipes. In the oil separator (126) the oil is filtered and flows through the recirculation pipe (127) back to the cylinder head.
The pressure control valve in the cylinder head cover prevents excessive vacuum in the engine.
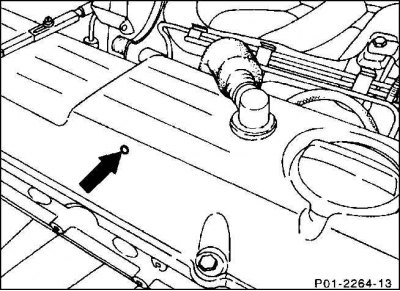
A vent hole is provided in the pressure control valve in the cylinder head cover to ventilate the diaphragm space (arrow). It should not be clogged with dirt or preservatives.
