It consists of a ceramic monolith 2 with a honeycomb structure, covered with a protective layer (see illustration 2.0). On the protective layer there are salts of noble metals, which provide the process of cleaning the exhaust gas.
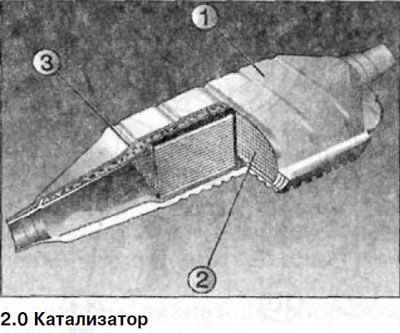
In the catalyst housing 1 there is a support insulator 3 which simultaneously compensates for thermal expansion.
Gasoline engines
Thanks to the electronic control of the fuel injection system, in combination with information from the lambda probe, fuel is injected into the combustion chambers in a dosed manner so that the catalyst can reduce the level of harmful substances in the exhaust gas.
The lambda probe is an electrical sensor that reacts to the content of oxygen residues in the exhaust gases by fluctuations in electrical voltage, which ultimately allows the control unit to evaluate the composition of the fuel-air mixture.
The injection system control unit can change the ratio of fuel and air in a fraction of a second.
On the one hand, this is necessary because operating conditions are constantly changing («full throttle», idling), and on the other hand, because afterburning in the catalyst occurs only when the exhaust gases contain a sufficient proportion of gasoline.
Diesel engines
In contrast to the catalysts installed on gasoline engines, vehicles with a diesel engine are equipped with 2 non-adjustable catalysts, because. more air is supplied to the diesel engine than is needed for combustion.
Such a catalyst converts carbon monoxide and hydrocarbon compounds contained in the exhaust gas into carbon dioxide CO and water (N2 O). In addition, it neutralizes the smell of burnt fuel characteristic of a diesel engine (see illustration 2.1).
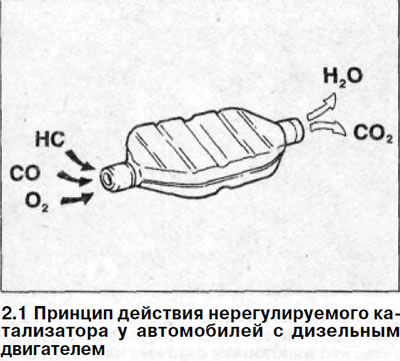
High content of nitrogen oxides (NO x) in the exhaust gases is reduced as a result of the operation of the exhaust gas recirculation system.
The EGR valve is located on the intake manifold and is actuated by low pressure.
The valve ensures that part of the exhaust gases are diverted back to the combustion chambers in order to lower the ignition temperature of the fuel-air mixture and thereby reduce the content of harmful substances in the exhaust gas.
