The oil pump sucks engine oil from the oil pan through the strainer and pumps it into the main oil line through the oil filter. There is a pressure reducing valve on the pressure side of the oil pump.
If the oil pressure is too high, the valve opens and some of the oil can drain back into the oil pan (see illustrations 9.0).
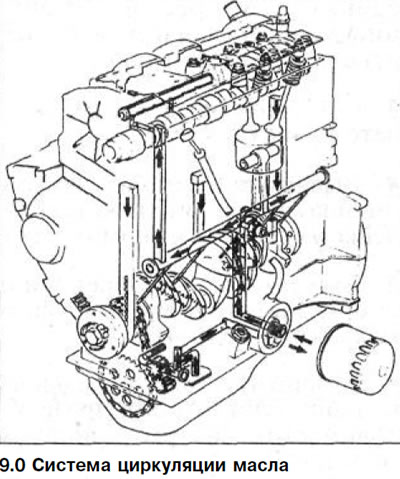
Through the central hole of the filter element, the filtered oil enters the pressure lubrication line. If the oil filter is clogged, unfiltered oil is sent to the pressure line through the bypass valve.
From the pressure lubrication line, oil flows through the pressure channels to the crankshaft bearings.
Through inclined holes in the crankshaft, oil enters the connecting rod bearings and from there is sprayed onto the piston pins and the pistons themselves.
At the same time, engine oil enters the cylinder head through the injection pipes to the camshaft bearings and the gas distribution valves (see illustration 9.0).
In diesel engines, as well as in vehicles A 190, engine oil is cooled using an additional oil cooler. This oil cooler is attached to the oil filter flange and is included in the coolant circuit.
Oil consumption
Oil consumption in internal combustion engines refers to the amount of oil that is produced as a result of the combustion process.
In no case should oil consumption be identified with oil losses that occur as a result of leaks due to leaks in the oil pan, cylinder head cover, etc.
Normal oil consumption occurs as a result of the combustion of small amounts of oil in the cylinders, the removal of residual combustion products and particles resulting from friction.
In addition, oil is consumed by the high temperatures and high pressures it is constantly subjected to in the engine.
In addition, the degree of oil consumption is influenced by external operating conditions, driving mode, as well as operating tolerances. Oil consumption should be no more than 0.8 liters per 1000 kilometers.
Attention! Do not fill oil above the maximum mark on the reservoir. If too much oil was poured during refueling, then remove or drain the excess. Otherwise, unburned oil entering the exhaust system may damage the catalyst.
