Precautionary measures
Do not disconnect the battery while the engine is running.
Do not short circuit the battery, i.e. do not connect positive (+) and negative (-) poles. If a short circuit occurs, the battery will heat up and may burst.
Do not expose the battery to naked flames. The electrolyte is corrosive. Avoid contact with eyes, clothing or skin. Wash it off with plenty of water if necessary.
Do not unscrew the caps on the battery with a central gas outlet when charging, but make sure that the battery vent hose is connected.
Let the battery thaw if it is frozen. A fully charged battery freezes at about -65°C, a half-discharged one at -30°C, and a fully discharged one freezes already at a temperature of about -12°C. Make sure that the case is not cracked on the thawed battery. A battery with a cracked case must be disposed of.
Charge the battery in a well-ventilated area or outdoors. When charging the battery without removing it from the vehicle, leave the hood open.
31. Remove the battery to charge it with a normal charger or a quick charger. If the battery remains in the engine compartment, then the terminals must be removed from the poles for charging.
Attention! If you charge the battery without removing the terminals from the poles, then damage the electronic control units of the car.
The temperature of the electrolyte when charging the battery must be at least +10°C.
Charger
32. Remove the battery, see relevant chapter.
33. Battery of the usual type. Check the electrolyte level before charging. Top up with distilled water if necessary.
If the charging current can be adjusted on the charger, then the charging current should be about 10% of the battery capacity.
This means that for a battery with a capacity of 50 Ah, the charging current should be about 5 A. The battery charging time is approximately 10 hours.
34. Connect the positive pole of the charger to the positive pole and the negative pole to the negative pole of the battery. The charger must be switched off at this moment.
35. Plug the charger into a wall outlet. If necessary, turn on the charger.
36. Check the temperature of the battery by touch, with the palm of your hand, if the battery is charged with direct current. The temperature of the electrolyte during charging should not exceed +55°C. If necessary, interrupt charging or reduce the charging current.
37. Turn off (if it is needed) charger after the battery is charged and unplug the charger from the mains.
38. Disconnect the charger wires from the battery.
39. Check the battery charge, see relevant chapter.
40. Install the battery in the car tray, see relevant chapter.
Accumulators without central gas outlet
41. Before charging, unscrew the plugs of the battery cells and put them on the holes. In this way, splashing of the electrolyte caused by gases formed during charging is prevented.
42. Charge the battery until intensive gas generation stops in all cells, and also until the increase in electrolyte density and voltage stops.
These indicators are compared with three measurements of electrolyte density and voltage, performed at an interval of 1 hour.
43. Let the battery stand for about 20 minutes after charging is completed, and only after the specified time has passed, screw the plugs into the holes of the cells.
Charging a discharged and sulfated battery
Batteries that have not been used for a long time, such as those that have been left on a car that has not been driven, gradually discharge and can also become covered with sulphate salt deposits.
The battery is considered to be heavily discharged if the open circuit voltage is less than 11.6V. «Battery - check».
Electrolyte (mixture of water and sulfuric acid) A heavily discharged battery consists primarily of water.
Attention! At negative air temperatures, such a battery may freeze, and its case may burst.
A heavily discharged battery is covered with deposits of sulfate salts. This means that the plate surfaces harden and the electrolyte acquires a whitish tint.
If a discharged battery is charged immediately after being discharged, salt deposits and plate hardening will continue, and the battery's ability to accept charging current will be limited.
A heavily discharged and sulfated battery should be charged with a small current. The charging current in this case should not exceed 5% of the battery capacity.
The charging current, for example, for a battery with a capacity of 60 A / h should be 3 A. The charging current voltage should not exceed 14.4 V.
Attention! A heavily discharged battery should not be charged with a quick charger.
Accelerated battery charging. Using the auxiliary battery
Boost charging or emergency engine starting using a booster battery should be an exception as the battery is exposed to a very high current in a short period of time.
With boost charging, the charging current is 20% or more of the battery capacity.
Batteries that have been stored for a long time and are heavily discharged should not be charged using a rapid charger, as they are then charged with a so-called surface charge.
Care of battery terminals
44. Check the battery terminals for signs of corrosion. Pole corrosion appears as white or yellowish powdery deposits.
45. Remove the battery.
46. Treat the battery terminals with a solution of water and soda. During the resulting reaction, the formation of bubbles will occur. The pins will turn brown.
47. Clean the conclusions (if necessary) wire brush or battery terminal cleaner.
48. After the reaction is completed, wash the terminals and the battery itself with clean water and let it dry.
49. Replace the battery.
50. Connect with the ignition off, the wire terminals to the battery poles.
51. Apply a thin layer of petroleum jelly or a suitable lubricant to the terminals to prevent further corrosion.
Attention! Do not lubricate the poles immediately before installing the power wire terminals on them.
Battery storage
If the car will not be used for more than 2 months, the battery should be removed and stored in a charged state. The most favorable storage temperature is from 0°С to +27°С.
At these temperatures, the battery is the least discharged. It is necessary to charge the battery no later than after 2 months of storage. Otherwise, the battery will become unusable.
If a battery that has been stored for a long time is charged from an accelerated charger, then it either does not accept the charging current or turns out to be allegedly charged with the so-called surface charge. Such a battery has all the signs of a faulty one.
Before a battery is considered defective, it must be checked.
52. Measure the density of the electrolyte. If the density of the electrolyte in all cells differs by no more than 0.04 g / ml, then the battery can be charged with a conventional battery charger.
53. Check the battery after charging under load, see relevant chapter. In the workshops, special devices are used for this. If the battery voltage is below 9.6V, then the battery is bad.
54. Check electrolyte density. If in one or two adjacent cells the density is significantly lower (for example, in 5 cells the density is 1.16 g/ml, and in one cell it is 1.08 g/ml), then the battery has a short circuit and is considered faulty.
55. Recharge a heavily discharged and sulphated battery.
Battery self-discharge
Depending on the vehicle configuration, the natural self-discharge of the battery is supplemented by current consumption by various control devices that continue to work even when the engine is turned off.
Therefore, the battery of a car that has not been used for a long time must be recharged at least every 6 weeks.
If there is a suspicion that there are leakage currents, then check the on-board electrical system as follows, using a charged battery:
56. Set the ammeter to the upper measuring range.
57. Disconnect the wire terminal from the negative pole of the battery «masses» (-).
Attention! When the battery is disconnected from the radio, the security code is deleted, as well as all automatic settings on the radio. Therefore, first read the provisions of the chapter «Battery - removal and installation».
58. Connect positive (+) ammeter lead to wire terminal «masses» (-), taken from the negative pole of the battery, and the negative (-) ammeter output - to the negative pole of the battery (see illustration).
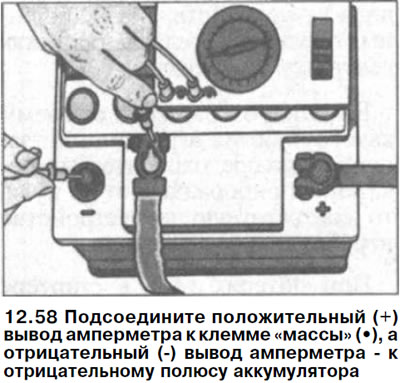
Attention! You can also check with a test light. But if the light bulb connected to the ground wire terminal (-) and the negative pole of the battery does not light up, then the test must be repeated using an ammeter.
59. Turn off all current consumers, turn off the clock (and other permanent consumers of electricity), close the doors.
60. Switch the ammeter to smaller and smaller measuring ranges until the ammeter starts to register voltage and the reading can be read (1-3mA are allowed).
61. Interrupt various electrical circuits by removing one fuse after another. If, when a circuit is disconnected, the ammeter readings drop to zero, the fault should be sought in this circuit. Its sources can be corroded or dirty contacts, frayed wires, internal short circuit in the circuit.
If no fault is found in fused circuits, disconnect wires from non-fused devices such as alternator and starter.
If, when disconnected from the terminals of any of the units that are not protected by fuses, the readings of the device drop to zero, then sort or replace the corresponding device.
In case of current losses in the starter or in the ignition system, it is imperative to check the ignition switch according to the diagram (workshop work).
62. Attach ground wire terminal (-) to the battery.
63. Set up an electronic clock.
64. Enter the security code into the radio.
